One-Stop-Shop provided by Public-Private-Partnership
Description
Public Private Partnerships (PPP) are a well-known delivery model in the construction sector, involving a contract between a public sector authority, the building owner, and a private contractor in charge of the management and the development of the building renovation project. The private party provides the service to the public authority, assuming substantial financial, technical and operational risks in the renovation project. This model is already widely used around the world, on a project basis, i.e. a new PPP is usually settled for each building (or set of buildings) to be renovated.
The Energy Performance Contracts (EPCs) where the public sector uses private energy service companies (ESCO) through Public Private Partnership arrangements, fits for instance in this category (more information can be found under the EPC description).
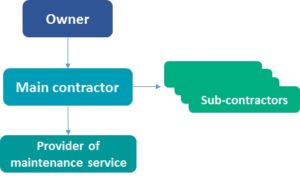
In this collaborative model, private and public partners collaborate coordinating their skills and knowledge for long term contracts (usually 20-30 years). The selected contractor involves designers, maintenance services providers and other subcontractors needed stipulating specific contracts with each of them, during the whole project duration, being the only contact point for the public building owner.
 PPP models are mostly used in very complex projects that require high level of integration. Since PPP delivery method is widely used around the world, many types of financing contracts may be used under this scheme: usually, for instance, the PPP contractor finances the initial investment and the client pays a constant fee for using the property during the contract. In some cases, a private sector consortium may create a special company called a “special purpose vehicle” (SPV) to develop, build, maintain and operate the asset for the contracted period.
PPP models are mostly used in very complex projects that require high level of integration. Since PPP delivery method is widely used around the world, many types of financing contracts may be used under this scheme: usually, for instance, the PPP contractor finances the initial investment and the client pays a constant fee for using the property during the contract. In some cases, a private sector consortium may create a special company called a “special purpose vehicle” (SPV) to develop, build, maintain and operate the asset for the contracted period.
PPP model are usually implemented in the case of multidisciplinary projects where team members have to strongly collaborate. Because of the mix of responsibilities and finance schemes, PPP delivery models provide opportunities for both public and private sector. However, PPP are complicated delivery models in the construction sector that require strong involvement of the different stakeholders, therefore PPP delivery method may cause an increase in time and cost of projects delivery and increase potential risks associated to the different steps of development.
"What” (value proposition)
Public Private Partnerships (PPP) business model provides the following advantages for the customer:
- The public owner identifying the need of a refurbishment of a public building contracts with a private contractor, in charge of the whole complex renovation project
- Simple structure with only two prime players: public owner and contractor
- The contractor has full responsibility for the design, construction, financing and final result achieved, assuming the relative risks
- Through the term of a contract, the government pays a guaranteed structured monthly fee that ensures financial predictability through a fixed cost of occupancy while avoiding unexpected costs and project delays
- The private contractor takes responsibility for functions such as operating and maintaining the building, with a long-term contract
"Who” (target customer)

Public building owners planning complex renovation projects that require high level of integration (e.g. administration buildings, schools, universities, hospitals etc.) and wish to include maintenance services over a long period in the same contract.
"How” (value chain, activities, resources)
The public owner has a single reference contact with the private contractor that is in charge of all the aspects of the project, including the choice of sub-contractors to perform design, construction and maintenance services during the renovation project and all over the contract duration (20-30 years)
"Why” (revenue model and cost structure)
Cost structure:
The financing system is that the PPP contractor finances the initial investment and the public owner pays a constant fee, usually monthly, for using the property during the contract.
Revenue streams :
The private contractor receives a monthly fixed fee from the owner.





