Standard envelope insulation – ‘light’
Building Characteristics
Building type
Type of ownership
Climate
Age Class
Cost Benefit Indicators
Embedded Technologies
Envelope
HVAC
Renewables
Energy management
Technology readiness
actual system proven in operational environment (with competitive manufacturing)
Description

This package consists in the very first step of the thermal insulation of a building and includes the following components:
- Roof insulation, using either an insulation panel/roll or a spray foam under the roof. External roof insulation is also possible (i.e. built-up roof insulation under waterproofing)
- Energy efficient windows (double or triple glazing)
Without proper insulation, as much as 25 to 30% of the heat in an uninsulated house is lost through the roof, and 10 to 15% through the window. Those two points are usually addressed first (i.e. before the walls – 25 to 35% of losses, and the floor – 10 to 15% of losses) as they are the most easy to deal with and the most profitable in the short term. Loft insulation and new windows act as a barrier, slowing the movement of heat out of the building during the winter and into it during the summer.
On its own,this package will not increase the performance of a building sufficiently for this building to become energy-efficient, but it can be complemented at a later stage with additional technologies so as to generate more substantial energy savings.
Roof / loft insulation
Materials
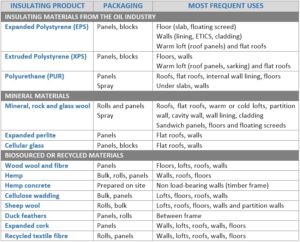
Different types of materials can be used for internal and external insulation, either in a roll, panel or spray foam form, each having its own benefits and limitations: wool (glass, rock, sheep or hemp), polyurethane, expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS). The recommended uses are the following:
Techniques
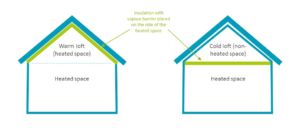
There are two main ways to insulate a loft or a roof: at the joists or at the rafters.
Insulation at the joists (Source: ADEME)
Cold loft insulation at the joists
The insulating material is laid (or sprayed) on the floor of the cold loft.
Warm loft insulation at rafter or externally
For the insulation of warm and occupied lofts under a pitched roof, two techniques are available:
Internal insulation
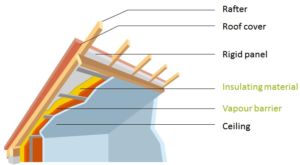
Insulation at the rafters with panels (Source: ADEME)
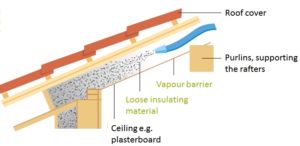
Loose fill insulation (Source: ADEME)
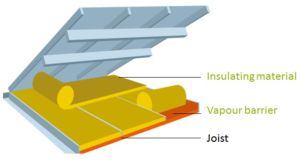
The internal insulation can be done with semi-rigid panels or rolls, whose layout will depend on the structure of the building frame and the available space.
A loose-fill insulation can also be injected in an air-tight cavity under the roof cover.
External insulation
Insulating from the outside avoid loosing living space but requires to remove the existing covering. Load-bearing panels can be used, or insulation can be added between the rafters and the roof covering, with a roof sarking (i.e. a protective and waterproof second skin under the roof). This last solution requires raising the roof line.
Flat roofs insulation
For flat roof, external insulation (“hot roof”) is recommended. Insulating from the inside can cause damage as it will inevitably lead to the formation of condensation. In this case, a rigid insulation is fitted outside, above the existing weatherproofing. This is then covered with a further weatherproofing layer.
Energy-efficient windows
Materials
The performance of the windows depends on the glazing and the frame. The level of performance is expressed by the thermal transmittance coefficient Uw. Performant solutions exist with timber, PVC or aluminium (with thermal breaks) frames.
Double glazing
Double glazing is made of two glass layers separated by an air gap. It is more performant than simple glazing and reduces the condensation and heat losses through the windows. The new generation of double glazing includes argon instead of air, as well as a fine transparent layer with low emissivity, usually silver-based: its insulating capacity is 2 to 3 times that of standard double glazing.
Triple glazing
Triple-glazing is made of three layers of glass separated by two layers of argon or krypton and two low-emissivity metallic layers. The Uw value is excellent, however the ligh transmittance can be lower than for a good double-glazing.
Techniques
Windows can be changed with two main techniques:
- By keeping the existing frame: this a simplest option, however the performance and the glazed area are slightly reduced
- By removing the existing frame: this is the most performant option, however it requires more work and some finishing
As double or triple-glazed windows will be more airtight than the original single-glazed frames, condensation can build up in the building due to the reduced ventilation. If there is not a sufficient level of background ventilation in the room, replacement windows should therefore have trickle vents incorporated into the frame, that let in a small amount of controlled ventilation.
Design and implementation
Strenghts
- Thermal properties that can be adjusted to climate and regulatory requirements
- Different available materials, including bio-sourced ones (hemp and sheep wool, timber framed Windows)
- Easy to install
- Low cost solution
- Common retrofitting solutions, well established in building codes and with extensive references
- Benefits in terms of acoustic comfort
Weaknesses
- Disturbance to building occupants (however no longer than a few days)
- The installation of windows should be done with care to avoid heat losses through draughts and termal bridges.
- The installation of insulating material should also be handled with care to prevent skin irritation during installation (for mineral wool) and minimise the risk of condensation (which would reduce the performance).
- Some of the insulating materials (e.g. hemp fibres) need to be treated with chemicals to give the insulation resistance to fire.
- Wooden frame windows require maintenance
Opportunities
- New thermal regulations
- Important market in Europe
- New insulation materials more environmental-friendly
Threats
- Fire regulations for EPS (e.g. phase out of flame retardant HBCD in Europe)
- EPS, XPS and PVC meet growing criticism (with regard to hazardous substances and combustibility)
Related Business model
One-Stop-Shop supported by a Step-by-Step approach
The Step-by-Step renovation model is a widely diffused model of building refurbishment that consists in the replacement of different building components (such as windows, plasterwork, roof covering, boiler etc.) according to their life duration.
One of the benefits of such an approach is that it gets the most out of each building component so that the initial investment is taken advantage of to its fullest. The need for replacements of various components arises at different points in time which means that in the case of a complete building retrofit, components that are still intact are renewed unnecessarily before their due time, leading to sub-optimal investments. With the step-by-step approach this can be avoided. When applying this approach, a building renovation plan should be made for all measures, including those which lie in the distant future, before starting the work. In this way, it can be ensured that an optimal end result is achieved in terms of cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency and quality.
Recommendations for replication
The step-by-step approach is probably the most likely to be replicated as it minimises the main obstacle to the process of energy renovation of buildings, i.e. the high initial investment. It is the approach that is most suitable for small investors with a prudent attitude, who aim to improve their living conditions and who do not immediately seek a significant increase in property value.
The main advantage lies in the possibility to check, after each intervention, the benefits in terms of comfort and energy savings, splitting the risk between smaller investments, as well as keeping the possibility to make corrections in the course of future interventions.
The important elements for the success of this business model are:
- Technical know-how of the OSS consultants who advise clients:The interventions carried out in the early stages will have to be compatible with the interventions planned in the future, possibly avoiding unnecessary redundancies, and therefore the allocation of costs in interventions that will not generate savings.
- High percentage of dwellings occupied by owners: Statistically, homeowners are more likely to carry out improvement works.
- Cumulation of incentives over time: In order not to decrease the interventions after the first one, it is essential that the incentives accrued during the various interventions are compatible and cumulative.
- Acceptable level of income and possibility to take advantage of incentives provided as tax deduction: As highlighted by Ameli & Brandt, 2015 the level of income is one of the parameters most closely related to the probability of investing in energy efficiency. Obviously, it has to be weighed against the cost of living, energy and, above all, the average cost of investment.